
The process that leads to pregnancy is relatively simple: The egg released from your ovary into the fallopian tube meets with sperm, and it becomes a fertilised egg which moves into your uterus to get attached to its lining, and the growth continues for the next nine months.
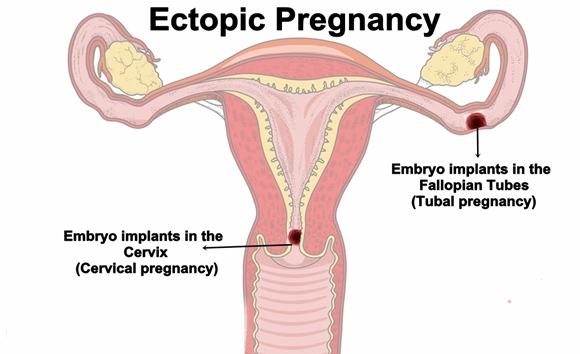
Whereas, an ectopic pregnancy happens when the fertilised egg gets attached in a place other than the inner part of the uterus. It is also known as tubal pregnancies because almost all ectopic pregnancy occurs in the fallopian tube. As the fallopian tubes aren’t designed to hold a growing embryo and hence the development of an embryo doesn’t happen properly in a fallopian tube, and it will require treatment.
The chance of occurrence of ectopic pregnancy is just 1 out of 50. Although it happens once in a blue moon, the egg might sometimes be implanted in the cervix, directly in the abdomen, in a C-section scar, in the ovary. Another possibility is, one egg may get the implant in your uterus whereas another in the tube or somewhere else. This condition is known as a heterotopic pregnancy, which is extremely rare.

Only 10% woman show no symptoms even with the condition of ectopic pregnancy and one-third show no medical signs. In most of the cases, the symptoms have very low specificity and will resemble those of other gastrointestinal and genitourinary disorders like salpingitis, rupture of a corpus luteum cyst, ovarian torsion or urinary tract infection, miscarriage, appendicitis. Standard symptoms are vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain. And both these symptoms are seen in less than 50 percent women. Usually, the pain is described as dull, crampy or sharp. If bleeding into the abdomen has occurred the pain may also spread to the shoulder. The severe bleeding may lead to shock, fainting or fast heart rate.
The causes for ectopic pregnancies may be as follows:
List of risk factors for an ectopic pregnancy is as follows:
Once you reach the hospital they will be doing a pelvic exam or pregnancy test to locate the pain, a mass in the abdomen, tenderness and an ultrasound test to ascertain if the uterus carrying a developing foetus might be done to view the fallopian tubes and uterus condition.
Based on your future plans for pregnancy and medical condition, the health care provider will decide on the best treatment once the ectopic pregnancy has been confirmed.
The treatment for the ectopic pregnancy might be any of the following:
The less damage you’ll have in the affected tube, and greater is the chance of a future successful pregnancy, the earlier you end an ectopic pregnancy. As long as your other tube is normal, you can still get pregnant without fertility treatment even if you lose one of your tubes. If the ectopic pregnancy was generated by an illness that is treatable like a sexually transmitted disease, getting the treatment for it can increase your chances of a successful pregnancy. Unfortunately, if your first ectopic pregnancy was the result of tubal ligation reversal, DES exposure or be damage from an infection, there is a major chance that your other might be damaged as well.
It is the most powerful creation to have life growing inside of you.There is no bigger gift