Cytomegalovirus (CMV), as name suggested is a virus causing disease, that may be transmitted to a developing child before birth. This infection is usually harmless and causes no long-term health consequences. Once a person gets infected, the virus remains alive, but is usually dormant within that person’s body for life.
There are two different types of infection: primary CMV and recurrent CMV infection. Primary infection causes more serious problems in pregnancy when compared to recurrent infection. However, in case of a weak immune system, the virus can become active and cause CMV disease.
Most children and adults who are infected with CMV do not develop symptoms. However, some people may experience the following symptoms:
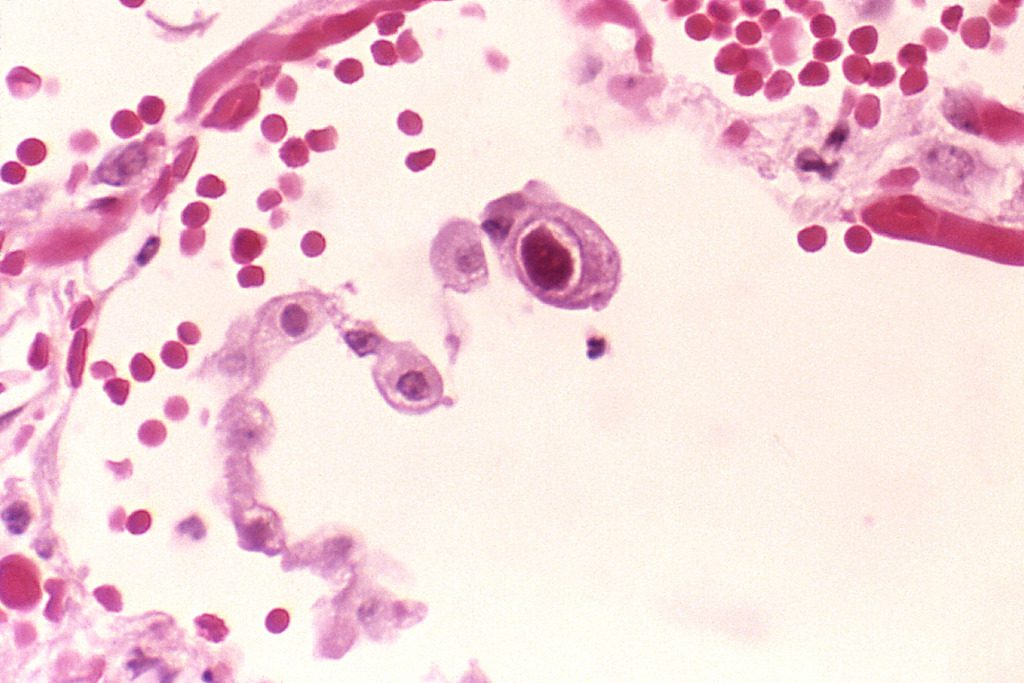
CMV is a member of the herpes virus group and is characterized by the ability to remain dormant within the body over a long period. Infectious CMV may be shed in bodily fluids intermittently, without any detectable signs or symptoms.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV):
The following groups are at an increased risk of this disease:
CMV is not associated with food, water, or animals and get transmitted from person to person and. CMV is not highly contagious but may spread in households and among young children in day care centers. The infection can be easily spread through close, intimate contact with a person excreting the virus in their saliva, urine, breast milk or other bodily fluids.
Most CMV infections are rarely diagnosed since the virus usually produces only few symptoms. However, people who have had CMV develop antibodies towards the virus and they will remain in their body for the rest of their life. A blood test can be done to determine the CMV antibody, which can be followed by another blood sample within two weeks.
The virus can be detected from specimens obtained from urine, throat swabs, and tissue samples. Laboratory tests to culture this virus are not widely available and are expensive. Amniocentesis is used to check fetal fluids or blood for signs of infection. Symptoms that denote possible infection include low amniotic fluid levels, intrauterine growth restriction, and enlarged tissues in the brain. Once the baby is born, testing can be done by using either saliva, urine, or blood.
It is the most powerful creation to have life growing inside of you.There is no bigger gift