Blood clots can impose serious effects while you are pregnant. A blood clot during pregnancy may possess additional risks or concerns since you are developing baby. However blood clots during pregnancy are rare and there is little need for concern and certain steps can be taken to minimize your rise of experiencing them while you are pregnant.
When the body sends cells, called platelets, to block the flow of blood a blood clot occurs. Normally, this occurs when you got a cut and to keep the injury from bleeding continuously. During pregnancy, there is more likely to clot as a safeguard against losing too much blood during labor.
However, a condition known as deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) happens when blood clots form in the legs and pelvic region and it is linked with a number of serious health concerns. But there are ways to both prevent DVT and to treat it after it occurs. Studies found that blood clots affect only 1 or 2 pregnant women out of every 1,000, so there is no need to worry, unless you feel uncomfortable.
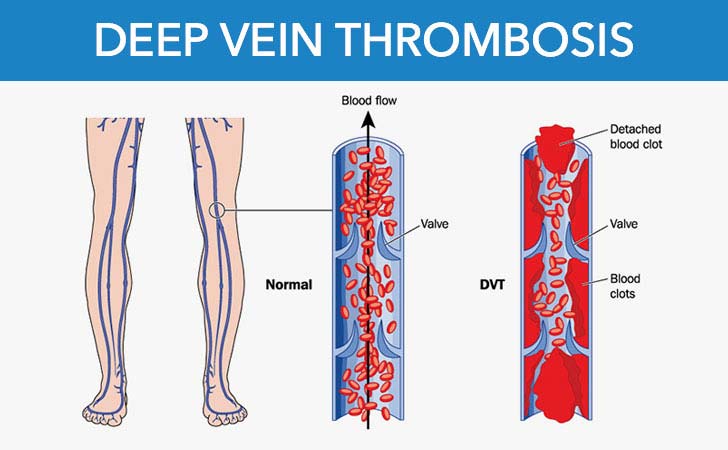
Women are most likely to experience a blood clot in their first three months of pregnancy or in the first six weeks after giving birth.
You could be at risk if:
Even though blood clots are unlikely, there are a few signs that can indicate the possibility of a blood clot.
These include:
DVT can affect your pregnancy in a number of ways:
Prevention of DVT can be achieved by a healthy lifestyle and staying active is a crucial component in combating DVT. Regular exercise improves circulation and increase ability of clot forming. It is also important to eat healthily and to quit smoking and other habits.
In the diagnosis stage of DVT, you are most likely to be treated with an anticoagulant, which hinders the blood from clotting as easily.
It is the most powerful creation to have life growing inside of you.There is no bigger gift